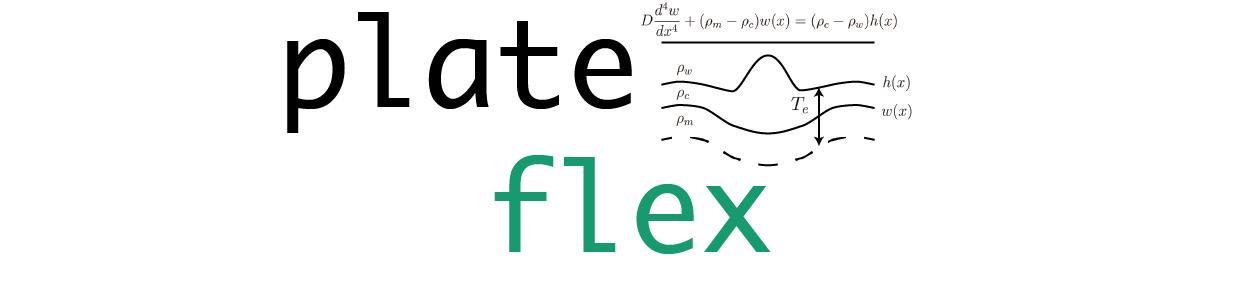
PlateFlex is a software for estimating the effective elastic thickness of the lithosphere from the inversion of flexural isostatic response functions calculated from a wavelet analysis of gravity and topography data.
Licence
Copyright 2019 Pascal Audet
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Installation
Dependencies
A fortran compiler
pymcseabornscikit-image(https://scikit-image.org)
See below for full installation details.
Conda environment
We recommend creating a custom conda environment
where plateflex can be installed along with its dependencies. This will ensure
that all packages are compatible.
Note
In theory, you could use your own fortran compiler. However, to ensure a proper installation, it is recommended to install fortran-compiler in the pflex environment.
conda create -n pflex -c conda-forge python=3.12 fortran-compiler pymc seaborn scikit-image
Activate the newly created environment:
conda activate pflex
Installing development branch from GitHub
Install the latest version from the GitHub repository with the following command:
pip install plateflex@git+https://github.com/paudetseis/plateflex
Jupyter Notebooks
Included in this package is a set of Jupyter Notebooks and accompanying data,
which give examples on how to create Grid objects and estimate
the flexural parameters over whole grids. The Notebooks describe how to
produce pulication quality results that closely match those published
in Audet (2014) and Kirby and Swain (2009) for North America, as well
as those of Kalnins and Watts (2009) for the NW Pacific.
These data and notebooks can be locally installed
(i.e., in a local folder Examples) from the package
by typing in a python window:
from plateflex.doc import install_doc
install_doc(path='Examples')
To view and run the notebooks you will have to further install jupyter.
From the terminal, type:
conda install jupyter
Followed by:
jupyter notebook
You can then save the notebooks as python scripts,
check out the model files and set up your own examples.
Global Variables
- plateflex.get_conf_cpwt()
Print global variable that controls the spatio-spectral resolution of the wavelet transform
Example
>>> import plateflex >>> plateflex.get_conf_cpwt() Wavelet parameter used in plateflex.cpwt: ----------------------------------------- [Internal wavenumber] k0 (float): 5.336
- plateflex.get_conf_flex()
Print global variables that control the setup of the flexural isostatic model
Example
>>> import plateflex >>> plateflex.get_conf_flex() Global model parameters currently in use by plateflex: ------------------------------------------------------ [Crustal thickness] zc (float): 35000 m [Mantle density] rhom (float): 3200 kg/m^3 [Crustal density] rhoc (float): 2700 kg/m^3 [Water density] rhow (float): 1030 kg/m^3 [Air density] rhoa (float): 0 kg/m^3 [Fluid density] rhof (float): 0 kg/m^3 [Water depth] wd (float): 0 m [Bouguer analysis?] boug (int): 1 ; True
Making gridded data
Packaged with this software is a set of topography, gravity and crustal structure data that
are easily imported into the PlateFlex package. Those data sets have been produced by
processing global grids of data from the
WGM2012,
GEBCO and
CRUST1.0 models using
GMT.
The WGM2012 models are used to extract Topography, Bouguer and Free-air anomaly data
over North America, and Free-air anomaly data over the NW Pacific.
The GEBCO model is used for the Bathymetry over the NW Pacific.
The CRUST1.0 models are used to extract the crustal thickness and crustal
density (corresponding to upper crust, or layer #6) over both North America and the NW Pacific.
Since those models are all defined using a different registration and grid sampling,
we use GMT to manipulate the grids and produce consistent data sets to use with
PlateFlex. We used GMT 5.4.1 in the following examples. These commands should be
copied to a bash script file and executed from the terminal.
WGM2012
These models are defined at a resolution of 2’ with a gridline registration.
# Set region and projection for North America. Use a transverse mercator
# with a central meridian of -95 degrees to minimize high-latitude distortions.
reg=-R-125/13/-28/58+r
proj=-JT-95/3i
# Make map of region
ps=Bouguer_NA.ps
gmt grdimage WGM2012_Bouguer_ponc_2min.grd $reg $proj -K -P \
-B10WSne -CPALET_WGM_Bouguer_Global.cpt -X1.5i -Y1.25i > $ps
gmt psscale -CPALET_WGM_Bouguer_Global.cpt -DJRM+o0.25i/0+e+mc -R -J -O >> $ps
# Project onto Cartesian grid with sampling interval of 20 km
gmt grdproject WGM2012_Bouguer_ponc_2min.grd -GBouguer_NA.grd $proj $reg -D20 -Fk
# Save grid information as header for use with PlateFlex software
gmt grdinfo -C Bouguer_NA.grd > header.txt
sed 's/^/# /g' header.txt > Bouguer_NA.xyz
gmt grd2xyz Bouguer_NA.grd >> Bouguer_NA.xyz
You can repeat these commands for the corresponding Free-air anomaly and Topography data.
GEBCO
This model is defined on a very fine grid (15” resolution) with a gridline registration. We first resample the grid onto a 2’ grid.
# Set region and projection for NW Pacific - here we use a regular
# Mercator since it straddles the equator.
reg=-R145/215/-15/45
proj=-JM3i
# Resample on a 2' grid
gmt grdsample GEBCO_data/GEBCO_2019.nc -GGEBCO_resampled_2m.grd -I2m -Rd
# Make map of region
ps=Bathy_PAC.ps
gmt grdimage GEBCO_resampled_2m.grd $reg $proj -K -P \
-B10WSne -CPALET_WGM_ETOPO1_Global.cpt -X1.5i -Y1.25i > $ps
gmt psscale -CPALET_WGM_ETOPO1_Global.cpt -DJRM+o0.25i/0+e+mc -R -J -O >> $ps
# Project onto Cartesian grid
gmt grdproject GEBCO_resampled_2m.grd -GBathy_PAC.grd $proj $reg -D10 -Fk
# Dump grid onto ASCII file with header
gmt grdinfo -C Bathy_PAC.grd > header.txt
sed 's/^/# /g' header.txt > Bathy_PAC.xyz
gmt grd2xyz Bathy_PAC.grd >> Bathy_PAC.xyz
CRUST1.0
The CRUST1.0 model is defined on a very coarse grid (1 degree). This is not a problem as we only use those fields in the inversion step, and not in the calculation of the wavelet transform. However, we still require an identical grid specification, so the first step is to resample them on a fine grid using spline interpolation.
Note
You first need to extract the proper layer within CRUST1.0. For crustal thickness, the weblink contains a global grid of crustal thickness (crsthk.xyz). For the density layer, you will have to use the provided fortran code getCN1xyz.f and rename the output file xyz-ro6 to something like crustal_density.xyz (for example). Layer 6 corresponds to the upper crustal layer. See the weblink for details.
# Set region and projection for North America
reg=-R145/215/-15/45
proj=-JM3i
# Create 2 .grd file from the ASCII data
gmt xyz2grd crsthk.xyz -Gcrust_thickness_1deg.grd -Rd -I1 -T
# Resample on a 2' grid using spline interpolation
gmt grdsample crust_thickness_1deg.grd -Gcrust_thickness_2m.grd -nb -Rg -I2m
# Make map of region
ps=Crust_thick_PAC.ps
gmt makecpt -Chaxby -T5/30/1 > crust.cpt
gmt grdimage crust_thickness_2m.grd $reg $proj -K -P \
-B10WSne -Ccrust.cpt -X1.5i -Y1.25i > $ps
gmt psscale -Ccrust.cpt -DJRM+o0.25i/0+e+mc -R -J -O >> $ps
# Project onto Cartesian grid
gmt grdproject crust_thickness_2m.grd -Gcrust_thickness.grd $proj $reg -D10 -Fk
# Dump grid onto ASCII file with header
gmt grdinfo -C crust_thickness.grd > header.txt
sed 's/^/# /g' header.txt > crustal_thickness_PAC.xyz
gmt grd2xyz crust_thickness.grd >> crustal_thickness_PAC.xyz